Fioricet is supplied in hard-gelatin capsule form for oral administration.
Each capsule contains the following active ingredients:
Butalbital, USP……………………50 mg
Acetaminophen, USP…………….300 mg
Caffeine, USP……………………..40 mg
Inactive Ingredients: sodium lauryl sulfate, talc, microcrystalline cellulose, stearic acid, FD&C red # 40, titanium dioxide, FD&C blue # 1,FD&C yellow # 6, gelatin.
Butalbital (5-allyl-5-isobutylbarbituric acid), is a short to intermediate-acting barbiturate. Acetaminophen (4´-hydroxyacetanilide), is a non-opiate, non-salicylate analgesic and antipyretic. Caffeine (1,3,7-trimethylxanthine), is a central nervous system stimulant.
They have the following structural formula:
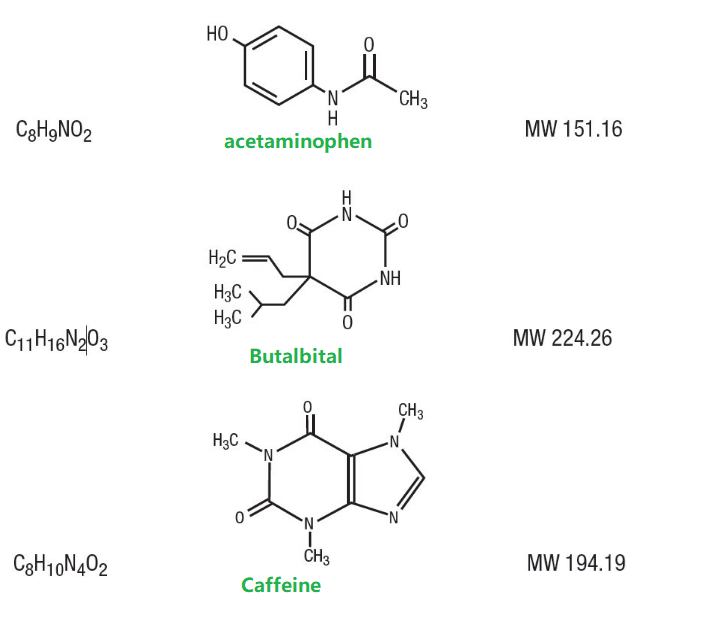
- Fioricet Chemical Structure
How should this medicine be used?
The combination of acetaminophen, Butalbital, Caffeine comes as a capsule and tablet to take by mouth. It usually is taken every 4 hours as needed. Follow the directions on your prescription label carefully, and ask your doctor or pharmacist to explain any part you do not understand. Take acetaminophen, Butalbital, Caffeine exactly as directed. Do not take more than six tablets or capsules in 1 day. If you think that you need more to relieve your symptoms, call your doctor.
Fioricet is indicated for the relief of the symptom complex of tension (or muscle contraction) headache. Evidence supporting the efficacy and safety of this combination product in the treatment of multiple recurrent headaches is unavailable. Caution in this regard is required because butalbital is habit-forming and potentially abusable.
This medication can be habit-forming. Do not take a larger dose, take it more often, or for a longer period than your doctor tells you to.
What special precautions should I follow?
Acetaminophen has been associated with cases of acute liver failure, at times resulting in liver transplant and death. Most of the cases of liver injury are associated with the use of acetaminophen at doses that exceed 4000 milligrams per day, and often involve more than one acetaminophen-containing product.
Before taking acetaminophen, Butalbital, Caffeine,
-
-
- tell your doctor and pharmacist if you are allergic to acetaminophen, butalbital, caffeine, or any other drugs.
- tell your doctor and pharmacist what prescription and nonprescription medications you are taking, especially anticoagulants (‘blood thinners’) such as warfarin (Coumadin), antidepressants, antihistamines, pain medications, sedatives, sleeping pills, tranquilizers, and vitamins.
- Many nonprescription pain relievers contain acetaminophen. Too much of this drug can be harmful.
- tell your doctor if you have or have ever had liver disease, porphyria, or depression.
- tell your doctor if you are pregnant, plan to become pregnant, or are breast-feeding. If you become pregnant while taking this medication, call your doctor.
- you should know that this drug may make you drowsy. Do not drive a car or operate machinery until you know how this drug affects you.
- remember that alcohol can add to the drowsiness caused by this drug.
-
What special dietary instructions should I follow?
Acetaminophen, Butalbital, Caffeine may cause an upset stomach. Take this medicine with food or milk.
General
Fioricet should be prescribed with caution in certain special-risk patients, such as the elderly or debilitated, and those with severe impairment of renal or hepatic function, or acute abdominal conditions.
Information for Patients
This product may impair mental and/or physical abilities required for the performance of potentially hazardous tasks such as driving a car or operating machinery. Such tasks should be avoided while taking this product.
Alcohol and other CNS depressants may produce an additive CNS depression when taken with this combination product, and should be avoided.
Butalbital may be habit-forming. Patients should take the drug only for as long as it is prescribed, in the amounts prescribed, and no more frequently than prescribed.
For information on use in geriatric patients, (see PRECAUTIONS/Geriatric Use).
• Do not take Fioricet if you are allergic to any of its ingredients.
• If you develop signs of allergy such as a rash or difficulty breathing stop taking Fioricet and contact your healthcare provider immediately.
• Do not take more than 4000 milligrams of acetaminophen per day. Call your doctor if you took more than the recommended dose.
Laboratory Tests
In patients with severe hepatic or renal disease, effects of therapy should be monitored with serial liver and/or renal function tests.
Drug Interactions
The CNS effects of butalbital may be enhanced by monoamine oxidase (MAO) inhibitors.
Butalbital, acetaminophen, and caffeine may enhance the effects of: other narcotic analgesics, alcohol, general anesthetics, tranquilizers such as chlordiazepoxide, sedative-hypnotics, or other CNS depressants, causing increased CNS depression.
Drug/Laboratory Test Interactions
Acetaminophen may produce false-positive test results for urinary 5-hydroxyindoleacetic acid.
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
No adequate studies have been conducted in animals to determine whether acetaminophen or butalbital have a potential for carcinogenesis, mutagenesis or impairment of fertility.
Pregnancy
Teratogenic Effects
Pregnancy Category C: Animal reproduction studies have not been conducted with this combination product. It is also not known whether butalbital, acetaminophen, and caffeine can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman or can affect reproduction capacity. This product should be given to a pregnant woman only when clearly needed.
Nonteratogenic Effects
Withdrawal seizures were reported in a two-day-old male infant whose mother had taken a butalbital-containing drug during the last two months of pregnancy. Butalbital was found in the infant’s serum. The infant was given phenobarbital 5 mg/kg, which was tapered without further seizure or other withdrawal symptoms.
Nursing Mothers
Caffeine, barbiturates, and acetaminophen are excreted in breast milk in small amounts, but the significance of their effects on nursing infants is not known. Because of potential for serious adverse reactions in nursing infants from butalbital, acetaminophen, and caffeine, a decision should be made whether to discontinue nursing or to discontinue the drug, taking into account the importance of the drug to the mother.
Pediatric Use
Safety and effectiveness in pediatric patients below the age of 12 have not been established
Geriatric Use
Clinical studies of butalbital, acetaminophen, and caffeine capsules did not include sufficient numbers of subjects aged 65 and over to determine whether they respond differently from younger subjects. Other reported clinical experience has not identified differences in responses between the elderly and younger patients. In general, dose selection for an elderly patient should be cautious, usually starting at the low end of the dosing range, reflecting the greater frequency of decreased hepatic, renal, or cardiac function, and of concomitant disease or other drug therapy.
Butalbital is known to be substantially excreted by the kidney, and the risk of toxic reactions to this drug may be greater in patients with impaired renal function. Because elderly patients are more likely to have decreased renal function, care should be taken in dose selection, and it may be useful to monitor renal function.
What should I do if I forget a dose?
Take the missed dose as soon as you remember it. However, if it is almost time for the next dose, skip the missed dose and continue your regular dosing schedule. Do not take a double dose to make up for a missed one.
What side effects can this medication cause?
Acetaminophen, Butalbital, Caffeine may cause side effects. Tell your doctor if any of these symptoms are severe or do not go away:
-
-
- drowsiness
- upset stomach
- vomiting
- stomach pain
- depression
- lightheadedness
- confusion
-
If you experience any of the following symptoms, call your doctor immediately:
-
-
- skin rash
- itching
- difficulty breathing
-
If you experience a serious side effect, you or your doctor may send a report to the Food and Drug Administration’s (FDA) MedWatch Adverse Event Reporting program online (http://www.fda.gov/Safety/MedWatch) or by phone (1-800-332-1088).
What should I know about storage and disposal of this medication?
Keep this medication in the container it came in, tightly closed, and out of reach of children. Store it at room temperature, away from excess heat and moisture (not in the bathroom).
Unneeded medications should be disposed of in special ways to ensure that pets, children, and other people cannot consume them. However, you should not flush this medication down the toilet. Instead, the best way to dispose of your medication is through a medicine take-back program. Talk to your pharmacist or contact your local garbage/recycling department to learn about take-back programs in your community. See the FDA’s Safe Disposal of Medicines website (http://goo.gl/c4Rm4p) for more information if you do not have access to a take-back program.
It is important to keep all medication out of sight and reach of children as many containers (such as weekly pill minders and those for eye drops, creams, patches, and inhalers) are not child-resistant and young children can open them easily. To protect young children from poisoning, always lock safety caps and immediately place the medication in a safe location – one that is up and away and out of their sight and reach. http://www.upandaway.org
In case of emergency/overdose
In case of overdose, call the poison control helpline at 1-800-222-1222. Information is also available online at https://www.poisonhelp.org/help. If the victim has collapsed, had a seizure, has trouble breathing, or can’t be awakened, immediately call emergency services at 911.
What other information should I know?
Keep all appointments with your doctor.
Do not let anyone else take your medication. This medication is a controlled substance. Prescriptions may be refilled only a limited number of times; ask your pharmacist if you have any questions.
It is important for you to keep a written list of all of the prescription and nonprescription (over-the-counter) medicines you are taking, as well as any products such as vitamins, minerals, or other dietary supplements. You should bring this list with you each time you visit a doctor or if you are admitted to a hospital. It is also important information to carry with you in case of emergencies.
Brand names
-
-
- Alagesic®¶
- Americet®¶
- Anolor®¶
- Anoquan®¶
- Arcet®¶
- Dolgic®¶
- Dolmar®¶
- Endolor®¶
- Esgic®¶
- Ezol®¶
-
-
-
- Femcet®¶
- Fioricet®
- Fiorpap®¶
- G-1®¶
- Ide-cet®¶
- Isocet®¶
- Margesic®¶
- Medigesic®¶
- Minotal®¶
- Mygracet®¶
-
-
-
- Nonbac®¶
- Pacaps®¶
- Pharmagesic®¶
- Quala Cet®¶
- Repan®¶
- Tenake®¶
- Tencet®¶
- Triad®¶
- Two-Dyne®¶
- Zebutal®¶
-
Brand names of combination products
-
- Esgic® Plus (containing Acetaminophen, Butalbital, Caffeine, Codeine)
- Geone® (containing Acetaminophen, Butalbital, Caffeine)¶
- Orbivan® (containing Acetaminophen, Butalbital, Caffeine)¶
- Fioricet® with Codeine (containing Acetaminophen, Butalbital, Caffeine, Codeine)
- Phrenilin® with Caffeine and Codeine (containing Acetaminophen, Butalbital, Caffeine, Codeine)
-
Abuse and Dependence
- esgic Plus

-
Butalbital
Barbiturates may be habit-forming: Tolerance, psychological dependence, and physical dependence may occur especially following prolonged use of high doses of barbiturates. The average daily dose for the barbiturate addict is usually about 1500 mg. As tolerance to barbiturates develops, the amount needed to maintain the same level of intoxication increases; tolerance to a fatal dosage, however, does not increase more than two-fold. As this occurs, the margin between an intoxication dosage and fatal dosage becomes smaller. The lethal dose of a barbiturate is far less if alcohol is also ingested. Major withdrawal symptoms (convulsions and delirium) may occur within 16 hours and last up to 5 days after abrupt cessation of these drugs. Intensity of withdrawal symptoms gradually declines over a period of approximately 15 days. Treatment of barbiturate dependence consists of cautious and gradual withdrawal of the drug. Barbiturate-dependent patients can be withdrawn by using a number of different withdrawal regimens. One method involves initiating treatment at the patient’s regular dosage level and gradually decreasing the daily dosage as tolerated by the patient.
¶ This branded product is no longer on the market. Generic alternatives may be available.
Last Revised – 05/15/2019